Polymerbuske
It all started in 2006. Since then, Bushing MFG has been providing ultimate polymer bush solutions to the world.
Polymer bushing, also known as the self-lubricating bearing, is ideal for carrying heavy loads. Its low friction and wear-resistant qualities make it the best among others.
Bushing MFG is a one-stop solution for a wide range of polymer bush. We serve globally. Our competitive prices and efficient before and after-sales services have turned our customers into potential stable clients.
Bushing MFG – Your Go-to Polymer Bush Manufacturer in China
When it comes to supplying friction-less bearings with low maintenance properties, self-lube Bearing is the ultimate solution.
The oil-free polymer bush is available with variable backing materials like bronze, plastic, brass, and other iron-based materials.
Metal polymer bush is suitable for numerous industries including, Dessa lager har en självsmörjande funktion med mycket låg friktion och hög slitstyrka för att möta alla våra kunders behov, hydraulic systems, medical devices, construction machinery, och många fler.
Our R&D team works round the clock to bring innovation in the material and designs. At the same time, the quality control team checks the quality from raw material gathering to final packaging.
As we provide free samples before order confirmation. We value your time and money. For this reason, you may get quick deliveries at your doorstep.
Furthermore, we also provide OEM services. You can show us a sample or draft. Our qualified and experienced team will provide you with similar designs with some innovative changes (if required). we manufacture sliding plates, halvlager, trasttvättar, flänsade buskar, and cylindrical bushes out of polymer sleeve bushes in a variety of styles and shapes. It can also build any custom form or size to meet the needs of the customer.
In more than 40 countries, we supply high-quality polymer bush. We facilitate you with the flexibility of order. You may order in bulk or small MOQ.
For further queries, you may contact us. Our customer services team is available round the clock at your service.
Steel Polymer Bushing
Linear, oscillatory, and rotational movements are all possible with this steel polymer bearing. They are used in automotive, construction, and agriculture industries.
Polymer Plain Bearing
It is a low friction polymer plain bearing sleeve bush with CNC high wear resistance. It is applicable in manufacturing plants, machinery repair shops, and food & beverages.
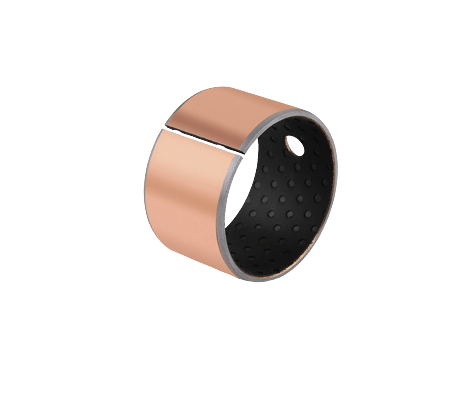

Polymer Bronze Porous Bushing
It is a bronze porous polymer oil-free self-lubricating sleeve bushing. You can use them in printing machinery, elevator, tobacco machinery, and fitness machinery.
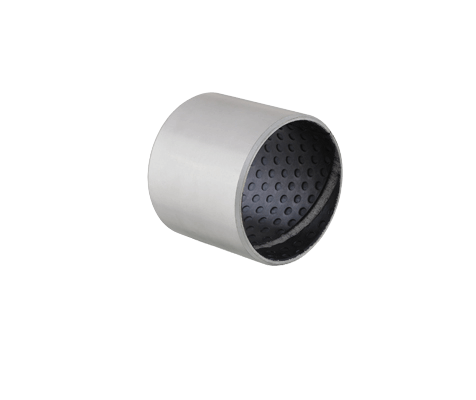

Mixed Carbon Self Lubricating Plastic Bushing
It is a wooden fiberglass fiber wounded PTFE mixed carbon plastic polymer bearing bushing that can be used in hotels, building material shops, and other manufacturing industries.
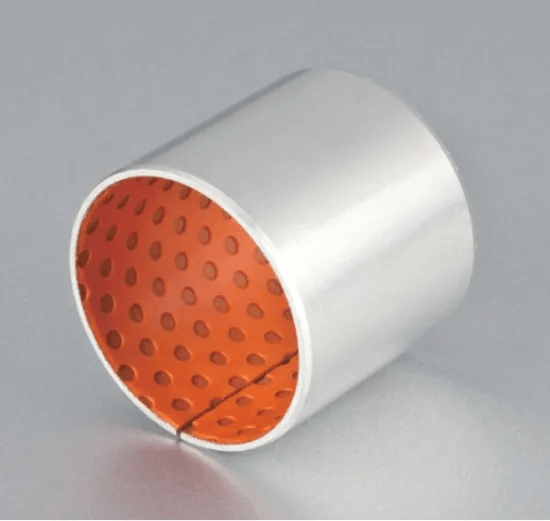

Metal Composite Polymer Bushing
It is a high-quality gear pump bushing metal-polymer composite bearing. You can use them in printing, woven, tobacco and gymnastic machinery, and pneumatic cylinder making industries.

Customized Polymer Bushings
Aside from the styles listed above, we can also create bearings based entirely on your specifications. You can also make adjustments to the designs shown above.
Polymer Bush – The Ultimate FAQ Guide
Your search for high-grade polymer bush is over. Welcome to the FAQ page of polymer bush by Bushing MFG.
Following are further details regarding the specifications, advantages, and uses of self-lubricating bearings.
1. What Is Polymer Bush?
Polymer bush minimizes equipment breakdown caused by component parts that aren’t greased.
A polymer bushing is employed in a machine or micro mechanism to convey rotational motion when at least one of two rubbing components is constructed of polymer.
Polymer bushings can be used in conditions that are hazardous to traditional bearings.
They have the ability to operate in hostile circumstances. The medium can be utilized as a lubricant in numerous situations.
Polymer bushing material is five times lighter than steel, lowering the weight and energy required to move them, as well as the amount of energy wasted due to friction because such bearings have a low friction coefficient even when not lubricated.
Polymers can also be used to create unique designs quickly and cheaply.
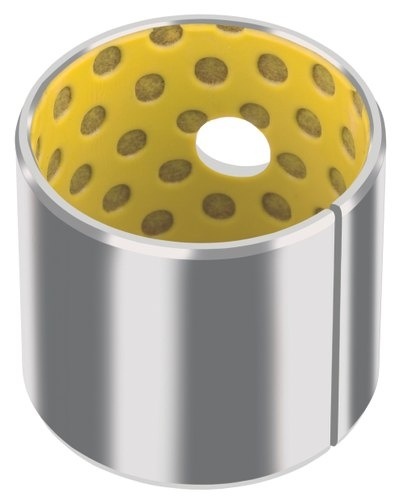

2. How Is the Polymer Bush Used?
Polymer bushings are used in a variety of applications.
They can be made of plain polymer (such as peek) or layered with PTFE mesh and an epoxy resin and glass fiber structure.
Polymer Bush Uses
You can use metal-polymer bushing in
- under operationen
- under operationen
- under operationen
- Forestry
- under operationen
- Construction machinery
- Water exposed applications
- Ships
- Vessels
Moreover, you can also use them in hydraulics and consumer electronics.
3. What Material Is Used to Make Polymer Bushing?
When choosing polymer bushing material, we must consider the maximum load, the system’s speed, and whether or not the system is lubricated.
The bushing’s load is the first factor to consider. This determines which materials will work best.
It’s critical to use a material with a minimum compressive strength rating to avoid failure under the most extreme loading conditions.
The industry standard is to add a safety factor to the bearing specification, allowing it to be utilized considerably beyond its design limit.
In order to make polymer bushing, different kinds of polymers are used.
These woven polymer bushings are comprised of PTFE and epoxy resin and have tensile strength far greater than injection-molded polymer bushings – and are far more resistant to heavy loads.

However, other polymer bushing material includes:
Steel
These bushings provide excellent fatigue resistance and load-carrying capacity, as well as good surface behavior and corrosion resistance.
It is a less expensive material than bronze and has a long service life. These bushings are made comprised of a steel tube that serves as a support, as well as a babbitt that is spun cast into the tube.
Its conformability and embed ability protect the shaft against harm, such as scoring from contaminates in the lubrication oil or fluid.
For intermittent dry starts, these bushings can be coated with a dry film lubricant or fluoropolymer.
Bronze
This is a long-lasting substance that is ideal for low-speed, high-load, severe-duty applications.
Copper
This type of bushing is usually made of bronze with tin, aluminum, or silicone added to it.
It has exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in maritime and other harsh situations.
Iron
Bushings made of cast iron are commonly used to support a hardened steel axel.
The friction coefficient is so low, the cast iron “glazes over” during usage, resulting in minimal wear and long service life.
Nylon
These bushings can be found in both dry and wet applications, such as transmission shift linkages. The axel supports some transmissions. Nylon, Teflon, Urethane, and Vespel are all common materials.
4. What Are the Types of Polymer Bushing?
Polymer bushings support shafts, limit movement along one or more axis, and minimize friction between contact surfaces.
The first step in choosing an appropriate metal-polymer bushing is determining what sort of bushing you require, which is usually determined by the loads that the bushing must support.
Polymer Bush Types
There are three types of polymer bearings available for this purpose:
- Bushings with sleeves
- Bushings with flanges
- Bushings for thrust
Bushings with Sleeves
The simplest design is sleeve polymer bushings. They appear to be a simple sleeves that can and cannot be divided.
The division or split simplifies installation and helps lessen the effects of dimensional changes caused by temperature fluctuations.
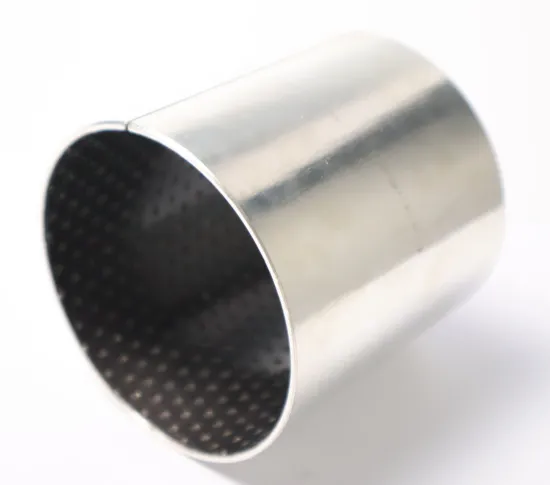

Polymer sleeve bearings are suitable for rotational, linear, or oscillating shafts, although they can only withstand radial loads.
Bushings with Flanges
Flange bush polymer bearing is similar to sleeve bushings but has a flange at the base.
They can withstand radial loads and axial loads as well.
They come in a split design, just like the sleeved bushings.
Thrust Bushing
Thrust polymer bushings resemble a simple washer in appearance.
They are employed to prevent metal-to-metal contact and are only meant to support thrust stresses.
5. What Is the Difference between Polymer Bushing and Coupling?
The difference between polymer bushing and coupling is as follows.
Polymer Bushing
- Polymer bushing is a cylindrical lining meant to reduce friction and wear inside a hole, which is frequently used as a casing for a shaft, pin, or hinge.
- An elastic bearing, usually constructed of rubber, that acts as a vibration isolator. An interface between two pieces that dampens movement and transmits energy.
- A threaded bushing is a fastening element that is put into an object to create a threaded hole in softer or thinner materials.
- A liner for a conductor’s passage through an opening, providing insulation and mechanical protection to the conductor.
- An adapter for connecting pipes of various sizes.
- The process of inserting polymer bushes, or linings, into holes or areas where wear is expected or friction is to be reduced, such as pivot holes.
Coupling
Coupling on the other hand, is the degree of reliance between two software modules. It also means the connection between two electronic circuits that allows a signal to travel between them.
A gadget that connects two or more items which work together to produce electricity or any required function.
6. Is Polymer Bushing and Bearing the Same?
Although bushing and bearing might sound the same they are different in many ways.
Polymer Bushing VS Bearing
Bearing
Bearing is a mechanical term that refers to the process of transferring a load’s energy between a wheel and an axle.
A bush polymer bearing is a device that is installed inside a wheel to reduce friction between the wheel and the axle.
By decreasing needless friction between two surfaces, a bearing enables for simpler motion. Metal-on-metal contact is abrasive and degrades the substance.
Instead of grinding against each other, bearings allow the two surfaces to roll over one other. A smooth ball or roller rolls against an inner and outer surface in a bearing.
The load is taken up by the ball or roller, which allows the device to spin.
Polymer Bushing
Bushings are fashioned like a tube or sleeve, and instead of rolling like most bearings, they help with a motion by sliding.
Polymer bushings, on the other hand, are a form of bearing since they help with rotational efficiency.
They’re designed to glide over rods and produce a low-friction motion. They provide great shock absorption while also reducing energy consumption, noise, and wear.
For heavy-duty wheels with tight load-bearing tolerances, polymer bushings are commonly employed.
Polymer bush lubrication is not required in these small tools, making them excellent for low- or no-maintenance applications. A consistent pattern of indents on the surface of the bushing acts as grease reservoirs, allowing the bushing to self-lubricate.
Some nylon bushings do not require lubrication. This makes them particularly helpful in the food and textile sectors, where dry applications are favored.
7. What Are High Load Polymer Bushing?
When working with heavier weights at slower speeds, polymer bushings are frequently used.
Durable bushings on industrial metal wheels can sustain significant load transfers and stress loading.
When it comes to bushings, frictional heat build-up must be taken into account. Heat is influenced by two key factors that are unit pressure and surface velocity.
Pressure velocity is the product of unit pressure and surface velocity.
To see if a bushing is suitable for a given application, look up the manufacturer’s limiting PV value.
The computed PV value of the application must be less than the manufacturer’s limitation PV value for safe operation.
Moreover, due to a combination of a duplex surface treatment and a particular surface topography, Polymer bushings have outstanding wear and seizure resistance.
This cross-hatching pattern creates enormous grease reservoirs in the loaded area and allows abrasive particles to be removed.
High pressure, abrasion, shocks, and corrosion are all suitable operating conditions for these bushings. They function admirably under high static loads and with modest oscillation movements.

8. How Can I Select Polymer Bushing?
Selecting for polymer bushing is much of a task. You must go through proper studies before buying any.
Here are a few tips you can use to buy polymer bush.
Dimensions
Determine the bushing dimensions to begin the bushing selection procedure.
One factor to consider is the bushing internal clearance, which is the radial clearance between the bushing and the shaft. This allows you to choose the bearing sleeve’s inner and outer diameters.
The length of the bushing is also required, but it may be referred to as the thickness in the case of a thrust bushing.
Load Bearing Capacity
The next stage in choosing a bushing is to define the expected load in order to calculate the load-bearing pressure. The load includes external direct loads as well as secondary factors such as:
- axial stresses that are not concentric
- The weight of what the bushing is supporting is deflected by side-loads.
Depending on whether the bushing is predominantly carrying an axial load or a thrust load, the projected area is computed accordingly. The pressure is then calculated by dividing the estimated load by the bushing’s projected area.
Furthermore, you must consider the following questions.
- What is the shaft material and how is the shaft finished?
- Will there be any lubrication?
- What will the operating temperature be?
Is the bearing subjected to abrasive, erosive, or chemically hostile environments?
9. How Can I Install the Polymer Bushing?
Polymer bushings are also easy to install and remove. The polymer bush design is shaft friendly and they are oil and fuel resistant.
It’s critical to use the correct bushing driver or installer when installing a bushing.
The installer must be the right size and have a smooth surface that will not damage the bushing. Prior to installation, most techs lightly lubricate the area of the bushing in touch with the installer.
Some technicians prefer to drive the bushing into place, while others prefer to use a press. Arbor press installation is preferred whenever possible since it decreases the risk of bushing breakage.
Bushings are important for the shaft and housing alignment. It is also important for seal alignment, clutch, and gear train longevity.
You must lay your focus on the correct installation of the polymer bushing.
10. What Are the Advantages of Polymer Bearings?
The polymer bearings have numerous advantages. Some of them are discussed below.
- In the radial dimension, polymer-type bearings can be kept to very tight tolerances to give support without expanding the extrusion (E) gap unduly.
- Polymer bearings, such as filled Teflon, can withstand compressive loads of up to 1000 pounds per square inch. Up to 36,000 PSI for nylons and 50,000 PSI for polyester fiber with resin.
- Excavator hydraulic cylinders frequently use greater compression materials since they are subjected to extreme side and shock stresses. However, filled Teflon materials work well in most situations.
- Bearings are available in two types: solid and split. Split bearings, when designed appropriately, provide similar support while improving installation possibilities without sacrificing performance.
- When placed on the outboard side of a rod groove, solid bearings, also known as bushings, are a good choice. When placing in a piston groove meant to function internally in a system, split bearings are required.
Because of their rigidity, nylon or composite bearings are usually trimmed to allow for installation. A Teflon bushing, on the other hand, can be fashioned into a ring or cut from a roll of the split strip.

11. Why Do Self-Lubricating Polymer Bushes Do Not Need External Lubrication?
Self-lubricating bearings are sometimes known as maintenance-free or greaseless bearings. They do not require relubrication or grease.
It’s crucial to note that self-lubricating bearings are not the same as for bearings that arrive pre-lubricated with grease or oil lubricant. Bearings that have been pre-lubricated will eventually need to be relubricated.
Self-lubricating bearings function by having lubricant impregnated within the bearing’s sliding layer.
Depending on the needs of the application, this lubricant might be liquid or solid. The lubricant is released through holes in the sliding layer as the bearing rotates, lubricating the bearing surface.
Even if the sliding layer becomes worn, the lubricant is equally disseminated across the sliding layer, resulting in no deterioration in low friction-bearing performance.
Before the impregnated lubricant reaches the bearing surface, a “running-in” area is frequently inserted at the top of the sliding layer to offer low friction bearing performance at start-up.
12. What Is Porous Bearing?
Porous journal bearings are comprised of an oil-impregnated porous bush that acts as an oil reservoir. It eliminates the need for an external oil source to lubricate the contact between a rotating shaft and a stationary bush.
The lubrication regime of bearings is influenced by the running conditions, dimensions, and physicochemical properties of the lubricant, as well as the permeability and pore size of the porous material, which should be hydrodynamic in the early stages of their life when the pores are almost full of oil.
They do, however, operate under mixed lubrication circumstances while starting and stopping, as well as when the oil in the pores has been lost after a period of use due to oil leakage and evaporation.
13. What Are the Features of Bushing MFG Self Lubricating Bearings?
The features of the self-lubricating polymer bush are
Reliability
The presence of oil minimizes the chance of seizure and allows the bearing to operate for thousands of hours without wearing out.
No lubricants
There is no need for lubricants and no maintenance is required.
Performance
Working pressures of up to 10 MPa and speeds of up to 8 m/s are possible.
The maximum operating PV is in the 10 MPam/s range, but it can be exceeded under exceptional circumstances.
The dimensional precision is exceedingly good (up to IT 5 in diameter) and the noise level is very low.
14. How Self Lubricating Bearings Are Made?
The ability of a bearing to transfer tiny amounts of the substance to the mating surface is known as self-lubrication.
This transfer procedure forms a layer that lubricates and decreases friction throughout the rail or shaft’s entire length. A self-lubricating polymer bush has various advantages over lubricated bearings.
The self-lubricating system forms through the following steps
- Lubrication is a necessary part of the bearing’s construction.
- The original bearing design does not include any lubrication (usually oil or grease).
- The lubricant will not degrade or become useless over time (lubricant aging).
- The lubricant is applied to the shaft surface in a consistent manner.
- Additional components do not increase the overall cost of the system.
Designad av bästa ingenjörer
